We also learned about types of organelles in a cell and what their function was. The nucleus keeps DNA inside it, controls the cell activities, and determines what type of cell it. The ribsome builds proteins. Vesicles move material around inside the cell. The rough endoplasmic reticulum, which has ribsome stuck to it, makes proteins and membranes that are going to be used in the cell. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum has no ribsomes stuck to it, and it produces lipids and cholesterol which are important in detoxification. The golgi appartus modifies and adds to the proteins that are transported to them via vesicles and sends out the finished proteins to parts of a cell or outside of the cell. The cytoskeleton is the structure inside the cell which gives it it's shape. The microtubles are the big wires that provide compression support. The microfilaments are the thin, small wires that provide tensonial support. The mitchondria generates energy, ATP. The vacuole are sacks that store things a cell might need later. The cytosol contains a solute inside it that dissolves material and fluids. The lysome contains degetsive enzymes inside it that are contained by a membrane. When these enzymes are released, they either break down a vesicles to get material or to kill the cell. Finally, the centriole sets up were other organelles are placed in relationship to itself.
Lastly, we learned about certain processes a cell goes through. It goes through the process of diffusion, which uses no energy, and causes molecules move in and out of the cell from high to low concentration till it reaches equilibrium. Another process only plant cells go through is photosynthesis, which produces 1 glucose, the sugar plants need for energy, and 6 oxygen, which is a waste project, which we need to breathe. The process animal cells go through to get energy is called cellular respiration. 36 ATP, the cell's main energy source, 6 carbon dioxide, and 6 water molecules are produced from this process.
Some setbacks I had was when I had to tell the difference between hypotonic and hypertonic diffusion, which I figured out by remembering hyper goes out and hypo goes in, and having to re-watch the photosynthesis podcast cause I got lost the first time. Some strengths I had were understanding and remaindering the different types of organelles and their functions, and being able to understand cellular respiration faster than photosynthesis.
From the experiences during this unit, I learned to pay closer attention to the vodcasts since they're becoming more complex. Thus makes me a better student since I will pay closer attention to vodcasts, making learning new concepts easier for me.
I want to learn more about the interowrokings of photosynthesis and cellular respiration in more detail. An unanswered question I have is where did the first cell come from. I wonder about how life first started on earth.
Plant Cell
http://www.wisegeek.org/what-are-some-organelles-in-the-cell.htm
Animal Cell
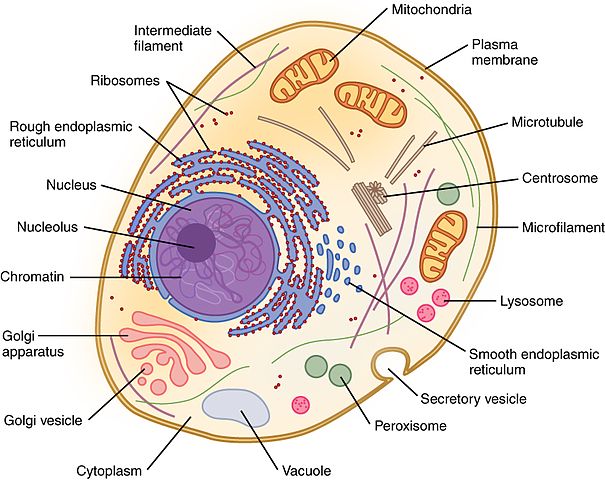
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:0312_Animal_Cell_and_Components.jpg
No comments:
Post a Comment